If you are an avid WordPress user, encountering WordPress errors is a usual thing. If you’ve ever encountered 403 Forbidden error error, you know how disappointing it can be to be denied access to a page or resource on your website. The good news is that this error is usually easy to fix, and with a little bit of troubleshooting strategies, your website can start running within minutes. In this blog, I’ll explain what a 403 Forbidden Error is, why it happens, and provide you with some simple steps to fix it. Whether you’re a seasoned WordPress user or a beginner, this guide will help you tackle this error and keep your website running smoothly.
What is a 403 Forbidden Error?
The 403 Forbidden Error is the HTTP status code that appears when you attempt to access a resource that you do not have permission to access.
Why does 403 Forbidden Error Occur?
In the context of WordPress, a 403 Forbidden Error can pop up when you try to access a page or resource that requires a certain level of permission, but you don’t have that permission. For example, if you try to access the WordPress admin dashboard without logging in, you’ll receive a 403 Forbidden Error. Common causes of the 403 Forbidden Error include:
- A corrupt .htaccess file
- Poorly coded plugins
- Incorrect file permissions
- Blacklisting

Different Versions of 403 Forbidden Error
- including HTTP Error 403
- 403 Forbidden error was found while trying to use an Error Document to handle the request
- Forbidden
- Error 403
- Forbidden: You have not been given permission to access [directory] on this server
Ways to fix a 403 Forbidden Error in WordPress
Fortunately, fixing a 403 Forbidden Error in WordPress is usually straightforward. Here are some ways you can follow to resolve the issue:
-
Examine your .htaccess file
Checking your .htaccess file should be your first step. Access to the directories and files on your website is managed by this file. An issue with the .htaccess file may result in a 403 Forbidden Error.
You’ll need to use an FTP client to connect to the server hosting your website in order to examine your .htaccess file.
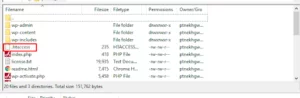
Once connected, go to your WordPress installation’s root directory and search for the .htaccess file. If you locate the file, give it a new name and try to visit your website once more. If the error disappears, there is probably an issue with your .htaccess file.
Then delete the file by right clicking on the file and create a new .htaccess file.
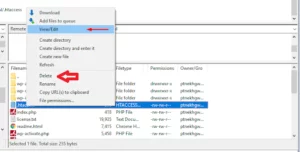
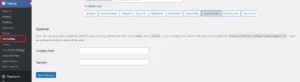
Go to Settings Permalinks in your WordPress dashboard (Nestify Dashboard below) to start a new .htaccess file.
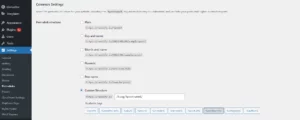
The “Save Changes” button is located on the page’s bottom. By doing so, the appropriate settings will be added to a new .htaccess file.
-
Check file permissions
Incorrect file permissions are yet another prevalent reason for 403 Forbidden errors. The server will deny access to the file if the file permissions are set incorrectly.
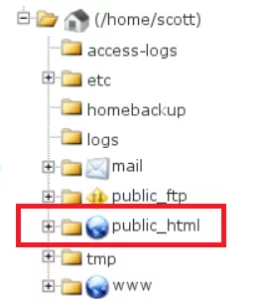
You must connect to the server hosting your website using an FTP client in order to check your file permissions. Once connected, go to the directory where the file you’re attempting to access is located. Depending on your FTP client, right-click on the file and choose “File Permissions” from the context menu.
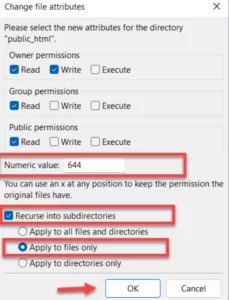
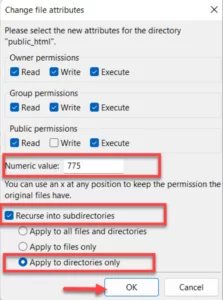
Ensure that the file’s permissions are set to 644 or 755. Change them if necessary, then try viewing the file once more.
-
Check plugins and themes
If neither of the above steps solves the problem, the issue may be related to a plugin or theme. To check if this is the case, you’ll have to deactivate all of your website plugins and temporarily work on a default WordPress theme (like Twenty Twenty-One).
To deactivate your plugins, go to your WordPress dashboard and navigate to Plugins → Installed Plugins. Select all of your plugins and choose “Deactivate” from the “Bulk Actions” dropdown menu.
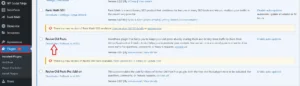
Once your plugins are deactivated, switch to the default WordPress theme.
If the error goes away, you know the problem is related to a plugin or theme. You can then reactivate your plugins one by one and switch back to your original theme until you find that peculiar factor causing the issue.
-
Clear your browser’s cache
One of the ways to resolve the 403 Forbidden error, the easiest step is to clear your browser’s cache. It’s also recommended to perform a hard refresh whenever you face any WordPress error.
The cause of 403 error could be due to your browser’s cached data. Therefore, clearing your browser cache and cookies or accessing your website in incognito mode may resolve the issue.
-
Hotlink protection
Hotlink protection is a valuable tool that safeguards your website images from unauthorized use by other websites. By activating hotlink protection, you can prevent Google Images, Pinterest, or any other site from displaying your images. Additionally, it can assist in reducing server resource consumption and site bandwidth.
However, if hotlink protection is not set up correctly on your CDN/hosting, it may result in a 403 error. Therefore, it’s crucial to configure it with care and verify the site’s status after implementation.
-
Reach out to your hosting provider
If you have religiously followed all the steps mentioned above but are still encountering the 403 error, reaching out to your hosting provider is your last option. Thankfully, numerous managed hosting providers are available to provide speedy assistance for such issues.
One such provider is Nestify, which offers round-the-clock live chat and ticket support for cloud-based WordPress hosting starting at just $12 per month. With Nestify as your host, you can rest assured that even the most daunting errors, such as the 403, will be handled expertly.
-
Consider Contacting Your Internet Service Provider
If your website is easily accessible to others, but you’re receiving a 403 forbidden error response, the issue may be with your internet service provider. It’s possible that your ISP or public IP address has been blacklisted due to some reason.
-
Whitelist your IP address on the server
Here are the steps to whitelist your IP address on a server to remove a 403 error:
1. Log in to your server or web hosting account.
2. Locate the security settings or firewall settings for your server. This can typically be found in the server’s control panel or through a command-line interface.
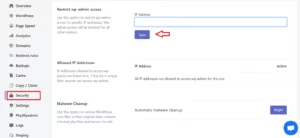
3. Add your IP address to the whitelist or allowed list. The specific steps for doing this depend on the server and firewall software you are using, but you may need to enter your IP address in a specific format (such as CIDR notation).
4. Save the changes to the firewall or security settings.
5. Test accessing the resource that was previously causing the 403 error. If the whitelist was configured correctly, you should now be able to access the resource without encountering the 403 error.
Conclusion
A 403 Forbidden Error in WordPress can be frustrating, but it’s usually easy to fix. By checking your .htaccess file, file permissions, and plugins and themes, you can quickly identify and resolve the issue if you’re still experiencing issues.
FAQs
Is a 403 Forbidden error always caused by something on my end?
No, a 403 Forbidden error can be caused by issues on the server side as well as the client side. While some causes of a 403 error may be related to your computer or internet connection, others may be due to server configuration or security settings.
Can a 403 Forbidden error be bypassed?
Attempting to bypass a 403 Forbidden error is not recommended, as it may be a violation of the website’s terms of service or may be illegal. Instead, you should try to resolve the issue by following the steps above or by contacting the website administrator for assistance.
Can a website visitor fix a 403 Forbidden error?
In most cases, a website visitor cannot fix a 403 Forbidden error as it is caused by server-side issues that are beyond the user’s control. However, a visitor can try clearing their cache and cookies and contacting the website administrator for assistance.
Is 403 Forbidden error the same as 401 Unauthorized error?
No, a 403 Forbidden error and a 401 Unauthorized error are different HTTP status codes. A 401 error indicates that the client needs to authenticate themselves before accessing the resource, while a 403 error indicates that the server has refused access to the resource regardless of authentication status.