Ecommerce payment processors allow merchants to connect their online store with a payment processing platform to accept and process payments for online transactions. These integrations typically involve installing or configuring a plugin, module, or API that connects the ecommerce platform with the payment processing platform.
In today’s digital age, payment processing has become essential to business operations. Choosing the right payment processing platform can significantly impact a business’s success.
Factors That Affect The Choice Of Payment Processing Platforms
- Type of Business
The nature of the business can significantly affect the payment processing platform choice. For example, a small e-commerce store might choose a payment processing platform for small businesses. In contrast, a large corporation might need a payment processing platform to handle a high transaction volume.
- Payment Methods
Different payment methods, like credit cards, debit cards, e-wallets, and mobile payments, need other payment processing platforms. A business should choose a payment processing platform that supports the payment methods that its customers use the most.
- Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are critical considerations in payment processing. A payment processing platform should have robust security to protect customer data from fraudulent activities. PCI-DSS compliance is a must-have for any payment processing platform.
- Integration and Customization
A payment processing platform should be easily integrated with a business’s other software and services. Additionally, it should have customizable features that fit a business’s unique needs. A payment processing platform that offers customizable branding can help create a seamless user experience.
- Fees and Costs
Payment processing platforms charge fees and costs for processing transactions. These fees can vary from platform to platform, and businesses must choose a payment processing platform that offers competitive rates. The platform’s pricing model should be transparent, and businesses must understand the fees they will be charged.
- Customer Support
Payment processing platforms should have excellent customer support that is available 24/7. Businesses must have a support system to help with technical issues or concerns.
- International Capabilities
For businesses that operate globally, payment processing platforms that support multiple currencies and can process international payments are critical. The platform should also have localized support and comply with international regulations.
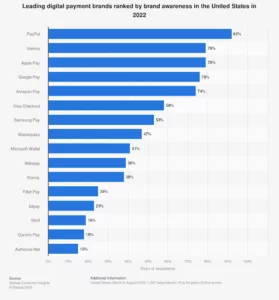
Best Payment Processors
1. PayPal
Founded: 2008 by Elon Musk and his team
Headquarters: California, United States
Global Users: 360 million active users
PayPal is a popular online payment processor that serves merchants of all sizes. Your customers will benefit greatly from using PayPal with your company. To accept payment via a buyer’s PayPal account, the seller must have access to the buyer’s credit or debit card details. Customers will appreciate the hassle-free transaction, and you may end up with repeat business.
Pros:
- Broad acceptance: PayPal is accepted by various retailers and online marketplaces.
- Safety: PayPal uses cutting-edge encryption technology to keep user data safe and prevent the buyer and seller fraud.
- Ease of Use: Customers can only sometimes input their payment and delivery information when using PayPal.
- Support: PayPal’s support many currencies means it can be easily used for purchases and donations across national borders.
Cons:
- Fees: PayPal charges for money to do certain transactions, such as receiving payments from buyers or sending money to loved ones.
- Limited availability: Not all countries use PayPal, and the service may have limits on the types of transactions that can be made.
- Customer service: Some users need help contacting customer support with questions or account problems.
- Risk of account freeze: Users run the risk of having their PayPal accounts frozen if PayPal suspects fraudulent activity or other violations of its terms of service.
2. Stripe
Founded: 2009 by Patrick Collison and John Collison
Headquarters: California, United States
Global users: 2 million users
In addition to PayPal, Stripe is a leading service provider for online merchants who need to accept credit card payments. Stripe allows you to build a custom payment API for your business. It’s difficult to design a user interface that non-technical users can understand.
Pros:
- Simple integration: With its well-documented APIs and developer tools, Stripe’s payment gateway is simple to incorporate into websites and applications.
- Multiple payment options: Credit cards, debit cards, mobile payments, and ACH bank transfers are just some of the payment methods that Stripe accepts.
- High security: With features like two-factor authentication and machine learning algorithms that detect and prevent fraudulent transactions, Stripe provides a high level of security for its users’ financial data.
- Fast payouts: Most transactions processed through Stripe are settled within two business days, making for quick payouts.
- Transparent pricing: Stripe’s pricing is clear and straightforward, with no surprises or mandatory minimums.
Cons:
- Complicated for nondevelopers: Stripe’s payment gateway may be complicated for non-developers, taking more time and effort to set up and administer.
- Transaction fee: For small businesses, Stripe’s transaction fees may be higher than those of other payment processors.
- Limited redressal: Merchants may need help with the Stripe dispute resolution process when resolving consumer disputes.
- Chargebacks: Stripe’s chargeback process can be confusing, costing businesses money.
- Limited support: Customer service for Stripe could be improved, making it difficult to acquire answers to concerns or resolve problems.
3. Amazon Pay
Founded: 2007 by the Amazon team
Headquarters: Washington, The United States
Global Users: 33 million users
Users are warming up to the Amazon Pay system because of the familiarity with the Amazon brand. This payment processing system simplifies transactions including mobile phone top-ups, bill payments, and online purchases. Since this method of payment is widely used, it is a good choice.
Pros:
- Simple checkout procedure: Amazon Pay’s straightforward process makes it easy for customers to make purchases swiftly and safely.
- Trusted platform: Amazon is a well-known, widely-used platform for online shopping, which helps inspire shoppers’ trust in the transaction process.
- Convenience: Amazon Pay makes it easy for existing Amazon consumers to shop on other websites by letting them use their existing Amazon account and payment information.
- Wide acceptance: Amazon Pay is a popular payment method since various online stores accept it.
- Buyer protection: Thanks to Amazon Pay’s buyer protection, protection against fraud or scams when making an online purchase is possible.
Cons:
- Limited merchant support: Amazon Pay’s effectiveness as a payment method could be limited if not all retailers and services supported it.
- Fee: Amazon Pay has transaction fees that may be greater than those of other payment processors, which can be a problem for small businesses.
- International acceptability issue: Amazon Pay might not be accessible in some regions or with some currencies, limiting its utility for cross-border purchases.
- Lacks flexibility: Amazon Pay may not be as flexible as other payment methods, which could be an issue for retailers who want a greater say over the customer experience during checkout.
- Customizability issues: It can be challenging to find answers to your queries or assistance with any problems you may encounter when using Amazon Pay due to the service’s minimal customer support.
4. Google Pay
Founded: 2015 by Google
Headquarters: California, The United States
Global Users: 55 million monthly active users
Google combined two disparate, enormous services—Android Pay and Google Wallet—into a single brand in 2015 under the name Google Pay. Google Pay is currently very popular and assists users in completing quick and secure payment transactions. Due to its user-friendly interface that is convenient for all users, Google Pay is well-liked. The merchant can accept customer payments using only their registered phone numbers.
Pros:
- Convenience: Google Pay allows users to quickly and easily transact using their mobile devices without carrying physical cards or cash.
- Security: Google Pay uses advanced encryption and tokenization technology to protect user information and prevent fraud.
- Rewards and promotions: Some credit and debit cards linked to Google Pay offer rewards or promotions for using the service, such as cashback or discounts at certain merchants.
- Integration with other Google services: Google Pay integrates with other Google services, such as Google Assistant, Gmail, and Google Chrome, making it a seamless part of the Google ecosystem.
Cons:
- Limited availability: Google Pay is not available in all countries and may have restrictions on certain types of transactions.
- Limited acceptance: While a growing number of merchants accept Google Pay, it may not be accepted everywhere.
- Fees: Google Pay does not charge fees for most transactions, but fees may be associated with using certain debit or credit cards.
- Privacy concerns: Some users may be concerned about Google’s collection and use of their personal information, including their transaction history.
5. Apple Pay
Founded: 2014 by Apple
Headquarters: The United States
Global Users: 382 million users

With its excellent payment processing features, Apple Pay, successfully introduced in the US, is now becoming famous everywhere. Apple Pay enjoys the same level of global trust as Google Pay and Amazon Pay. Due to its secure transaction capabilities, Apple is a well-known brand in payment processors worldwide. Similar to how Android Pay has grown in popularity, Apple Pay also offers cutting-edge conveniences in payment processing.
Pros:
- Convenience: Apple Pay allows users to make transactions quickly and easily using mobile devices without carrying physical cards or cash.
- Security: Apple Pay uses advanced encryption and tokenization technology to protect user information and prevent fraud.
- Wide acceptance: Apple Pay is accepted by many merchants, making it a convenient option for many people.
- Integration with other Apple services: Apple Pay is integrated with other Apple services, such as Siri and iMessage, making it a seamless part of the Apple ecosystem.
Cons:
- Limited availability: Apple Pay is not available in all countries and may have restrictions on certain types of transactions.
- Limited acceptance: While Apple Pay is accepted at many merchants, it may not be accepted everywhere.
- Fees: Apple Pay does not charge fees for most transactions, but fees may be associated with using certain debit or credit cards.
- Privacy concerns: Some users may be concerned about Apple’s collection and use of their personal information, including their transaction history.
6. GoCardless
Founded: 2011
Headquarters: United Kingdom
Global Users: 70, 000 businesses

GoCardless is one of a kind among online payment processors because it doesn’t require customers to use credit cards. It is regarded as the top debit card issuer to facilitate streamlined payment processing and monitoring of monetary dealings. GoCardless’s integration costs are lower than PayPal’s, saving money for the retailer.
Pros:
- Acceptance of multiple cryptocurrencies: BitPay allows merchants to accept payments in Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, Ethereum, and other cryptocurrencies.
- Low transaction fees: BitPay charges lower transaction fees than traditional payment processors.
- Quick settlement: BitPay settles payments in fiat currency within one or two business days, faster than other payment processors.
- User-friendly interface: BitPay provides an easy-to-use interface for merchants to manage cryptocurrency payments.
Cons:
- Limited currency support: While BitPay does support several cryptocurrencies, it doesn’t support all of them, which could be a limitation for some merchants.
- Regulatory risks: BitPay operates in a regulatory gray area since cryptocurrencies are not yet fully regulated in many jurisdictions, which could lead to legal and compliance risks.
- Security concerns: Like any cryptocurrency-related service, hacking or other security breaches are always risky.
- Limited customer support: Some users have reported issues with customer support and difficulty resolving payment disputes with BitPay.
7. Square
Founded by: Jack Dorsey and Jim McKelvey
Headquarters: California, The United States
Global Users: 24 million users
Square is expanding its global reach by building out a sophisticated payment processing infrastructure, and it already has offices in London, the United States, Canada, Japan, and many other places.
Square’s payment and human resource management services suite has attracted over 2 million businesses. You can accept payments from your customers quickly and easily with the help of Square’s user-friendly products, such as its chip reader.
Pros:
- User friendly: Merchants can easily accept payments thanks to Square’s intuitive interface.
- Multiple payment options: Credit cards, debit cards, mobile payments, and even online payments are all viable options for customers when shopping at a store that uses Square.
- Quick setup: Merchants can open a Square account and begin accepting payments in minutes.
- Integrations: Square has lower transaction fees than other payment processors and offers several helpful integrated features for small businesses, such as POS systems, inventory management, and invoicing.
Cons:
- Limited support: Some users have complained about problems with Square’s customer support, like a lack of response time and an inability to resolve payment disputes.
- Security: Hacking and other security breaches concern any payment processor.
- Witholding: Square’s practice of temporarily freezing merchant accounts when it suspects fraudulent activity is a headache for lawful enterprises.
8. Flagship Merchant Services
Founded in: 2001
Headquarters: San Fransisco, The US
Global Users: Not defined yet

The Flagship has built a solid reputation among payment processors worldwide thanks to the cutting-edge goods and services it provides from its base in Alabama. Flagship delivers on its promises by providing reliable payment processing for its merchants, making it an ideal choice for small and medium-sized enterprises. Flagship Merchant Services lives up to its name by being a reliable option for integrating your business’s payment procedures.
Pros:
- Multiple payment options: Flagship supports various payment options, including credit and debit cards, checks, and gift cards.
- Competitive rates: Flagship claims to offer competitive rates and will work with merchants to customize pricing plans based on their business needs.
- Customizable solutions: Flagship offers customizable solutions for businesses of all sizes and can integrate with various POS systems.
- 24/7 customer support: Flagship offers 24/7 customer support via phone, email, or live chat.
Cons:
- Hidden fees: Some merchants have complained about hidden fees with Flagship, particularly monthly and termination fees.
- Contract terms: Flagship’s contracts can be long and difficult to get out of, which can be problematic for businesses that need flexibility.
- Customer service issues: Some merchants have reported issues with Flagship’s customer service, particularly related to delays in getting issues resolved.
- Limited transparency: Some merchants have reported that Flagship’s billing statements can be difficult to understand, making it hard to identify errors or discrepancies.
9. Braintree
Launched in: 2007 by Bryan Johnson
Headquarters: Chicago
Global users: 5412 businesses
When it comes to connecting a company to a merchant account, Braintree is a common choice in payment processors list. PayPal integrated Braintree’s features in 2013 after purchasing the company. With all of PayPal’s bells and whistles, it makes ideal sense to team up with Braintree to receive the same high-quality payment processing choices as PayPal. Creating a vast selection of new merchant accounts is another feature made possible by Braintree.
Pros:
- Comprehensive payments: All major credit cards, debit cards, PayPal, Apple Pay, Google Pay, and more may be processed with Braintree.
- Robust APIs: Braintree’s API is a great option for programmers who wish to include payment processing into their apps or websites since it is straightforward and well-documented.
- Individualization: Braintree’s malleability to meet the needs of different businesses is a selling point for some customers.
- Fraud protection: Braintree’s state-of-the-art fraud protection features will help keep your company and your customers secure from unauthorized transactions.
Cons:
- Fees: Some vendors have complained that Braintree’s fees are higher than those of other payment gateways.
- Contract terms: Like many other payment processors, Braintree has a contract that might be difficult to get out of.
- Support: Some Braintree customers have voiced dissatisfaction with the company’s support staff, saying that they are either unable to resolve their issues or must wait too long for a response.
- Technical knowhow: Although Braintree API is well-documented, it may still require simplification for some in-house development teams.
Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, the payment processing landscape is evolving rapidly, with new payment methods and processing technologies emerging all the time. This creates exciting opportunities for businesses and consumers alike, but also highlights the importance of staying informed and up-to-date on the latest trends and best practices in payment processing.
Thus, payment processors are essential for the functioning of the modern economy, and their role will only become more important as commerce continues to shift towards digital channels. By working together with trusted payment processors, buyers and sellers can ensure that their transactions are completed securely and with minimal hassle, no matter where in the world they are located.
FAQs
What are the fees associated with e-commerce payment processing?
Fees associated with e-commerce payment processors vary depending on the payment gateway or processor used and the type of transaction. Fees may include transaction fees, gateway fees, chargeback fees, and currency conversion fees, among others.
What are some security considerations for e-commerce payment processing?
Security is a major issue for e-commerce payment processing, as sensitive financial information is being transmitted over the internet. It is important for businesses to use a secure payment gateway or processor, employ strong authentication methods, and comply with industry standards for data protection and privacy, such as PCI DSS.
How can businesses optimize their e-commerce payment processing?
To optimize e-commerce payment processing, businesses can focus on streamlining the checkout process, offering multiple payment options to customers, and utilizing fraud detection and prevention tools. Businesses can also seek out payment gateways and processors that offer customized solutions and competitive pricing.