In the technological world, we live in, new terms are often created to name and identify new features and technologies. So it is not uncommon to hear the name of some technology and not know its meaning. In this article, we’ll cover the cache, understand what it is and know your application when we talk about hosting websites.
Do you know what cache is? Have you heard of it, or would you like to know more about it? Follow us and find out all about this powerful feature that can speed up your website and reduce resource consumption on your hosting.
What is a cache?
In computing, Cache (pronounced késh) can be both a physical component (hardware) and a program (software) that stores data temporarily. The information stored in this system can be accessed quickly without any need for processing and searching the database. The Cache widely used in many types of electronic devices, including smartphones and personal computers.
In site hosting, the cache functions as a mediator, which sits between the user and the hosting server. So when a user browses a site, the system checks to see if they have a copy of the requested page. This occurs even before this request reaches the hosting server. If it exists, the copy is delivered to the user in a process that takes less time than is necessary to access the server and process the request.
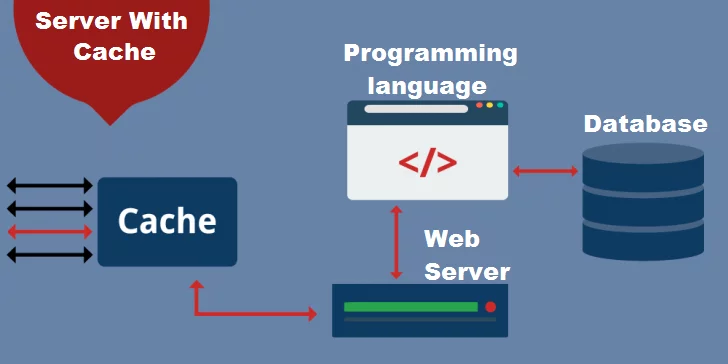
On a non-caching server, the operation is different, as shown in the figure below. In this case, all requests are processed on the server and other system items.
The service desk
To illustrate how it works, we can compare the cache system with a service desk. Imagine a serving room where there is a counter with some staff. Behind the counter, in addition to the employees who directly serve customers, there is also a manager. The manager does not answer the audience directly. From time to time, it may be necessary for one of the desk staff to take a determined issue for the manager to resolve.

Customers arrive at all times at the service counter, with different types of orders. In most cases, the customer solves your problem directly at the counter, by the employee who is there. However, counter staff cannot handle all orders. Some issues need extra evaluation or authorization, which can only be done by the manager. So, every 10 orders, 8 or 9 are settled directly at the counter. But 1 or 2 need to be taken to the manager, who resolves the issue and gives the solution to the employee. This, in turn, takes the solution back to the client.
In this fictitious scenario, the cache would be like the service desk, because it meets most requests, taking only a few to the server.
Now that we understand the concept and its operation, let’s take a look at the advantages of using it on a website.
Advantages of using cache on a hosting server
The main advantage of using such a system on a hosting server is speed gain. And in some cases, the loading time of a page can be 300 to 1000 times faster than a normal one.
Another great advantage is the reduced use of server resources. Because not all requests arrive on the server, resource consumption, such as memory and processing, is reduced.
Cache clean or refresh
Because of working with content copies, from time to time the cache needs to be refreshed or cleaned up. This becomes necessary whenever the content of the site or a page is updated. Otherwise, a visitor may encounter an old version of the page, which is cached.
In general, systems do this job of cleaning or renewing these copies automatically. In this case, the content copy is renewed whenever an update performed on the page. In some cases, renewal is done periodically, at regular intervals. This ensures that the stored content is always the latest. The automatic cache renewal process saves a lot of time and makes managing your website much easier. In many cases, the cache implemented in the hosting without you knowing and without having to worry about cleaning or renewal.
Cleaning can also be done manually. The process can vary and depends on the system used.
Types of cache used in hosting
Now, let’s take a look at some of the most common ways of using cache when we talk about the internet and websites.
Internet browser
Even the internet browsers such as Chrome, Firefox, and others, stores the copies of websites you have visited, in a system own browser cache. The goal is the same as mentioned above: speed uploading pages. When you visit any address on the internet, the browser checks to see if you already have a cached copy of the page in question. If it exists, it accesses the server only to verify that something has been updated on the page, displaying the user the stored content much faster than if it had to load the entire page again.
The browser storage system works for all the elements that make up a web page, which includes images, style files (CSS), scripts (JavaScript) and others. Images from a website, for example, are strong candidates to be cached. That way, if a site has the same image on several pages (such as a logo, for example), it does not always have to be loaded. A copy is used, in that case. The same goes for any script or file that is repeated in the various pages of a website.
Server hosting
In a hosting of sites, the caching system used between the user and the hosting server. Thus, before the server has to process any data, the requested content is sent to the user, if the copy of the data exists. Otherwise, the request took to the server.
This type of system can be used with any programming language and databases. Some web servers, such as NGINX and Apache, have built-in caching, with the goal of delivering content quickly and reducing the server’s processing load.
Most hosting companies currently offer such solutions on their servers. In this case, the cache can be installed or configured by default on the client-server. Because it is a resource that reduces the processing load of servers, it is desired for companies that their customers use this type of resource. If you do not know if there is a cache system in your hosting, please contact the company support. They will surely have this information. If this is the case, you can take advantage of the contact and request the installation of the service.
Varnish cache
The varnish is a cache-based acceleration system for websites. The system is free and open-source. Technically called an HTTP reverse proxy, Varnish can be installed on any server that has the HTTP protocol.
The manual installation of Varnish requires some technical knowledge. Despite this, many web hosting companies offer Varnish between their services, being able to be activated through the hosting control panel or having their installation requested. There are also some companies that have Varnish configured by default on all its servers, without the user having to make any kind of extra configuration to take advantage of this feature.
A curiosity: the word varnish was chosen in an allusion to the varnish that is applied to real objects to brighten and highlight their appearance.
Plugins for CMS

We cannot talk about websites without mentioning content managers. Also known as CMS, this type of system allows you to manage and publish content on a website, blog or virtual store. This is done through a friendly panel, without the need for technical knowledge.
Most content managers on the market allow the installation of plugins, which are pieces of software that add features and functionality to a CMS. Having a cache plugin in your CMS is virtually mandatory if you want to have an optimized website that loads quickly. This type of plugin generates complete copies of the pages of your site, serving them whenever necessary, in order to reduce the loading time of the pages of a website, virtual store or any web application.
Among the most popular plugins, we can mention W3 Total Cache for WordPress and JotCache for Joomla.
CDN
A content distribution network, or CDN, as its name implies, distribute a copy of its content among several servers around the world. Thus, when requesting the page of a site, the visitor receives the content cached in the data center closest to where it is located. In a traditional scenario, the user’s request would be directed to the origin server of the site, regardless of its location.
Because of this operation, CDN can accelerate the loading of a site in two aspects: both by caching the content of the site and by accessing a server that is physically closer to the user.
Conclusion
When a website’s performance is crucial to your business, every millisecond saved on page load counts in your favor. To help with this mission, a good cache system is critical.
In this article, we got familiar with cache concepts and their applications in the universe of web hosting. We have also seen the most popular types of use of this resource on the internet and we know possible applications.
If you have any questions about the subject, or just want to add information to the article, leave a comment and we will be happy to talk.