Lately, we talk much about this from the CDN, if Photon is a CDN if to speed up WordPress have to activate a CDN? But what is a CDN exactly? Do I really need it with WordPress?
Moreover, you should know what CDN is. It is currently one of the most important technologies of the Internet and the Web as we know it today and enjoys its work in part to the CDN.
Do I need a CDN?
To summarize…
You need a quick web, period. Do you need data?
- A survey conducted by Akamai showed that half of the Internet users expect a website to load in 2 seconds or less, and is very likely to abandon a site if it not loaded in 3 seconds.
- 79% of shoppers who have had difficulty buying online would never buy from that site again. And half of them would tell their friends about the unpleasantness of their experience.
- A recent study showed that a 1 second delay causes a 7% drop in conversions, 11% in page views and a 16% loss of customer satisfaction.
- And then we have the example of Google, which delivers millions of search results for any query in a quarter of a second, and shows on the top of the SERP sites that offer quality content, have authority, and are fast. If you do not meet any of these values, you lose points in the SEO, either.
If you have not yet realized, it is quite clear that a quick web is needed to succeed in business, and this is where the CDN comes into play.
Why? A CDN loads your site faster, which means better user experience and ultimately, help your site, your presence, your business grow.
Okay, so what exactly is the CDN?

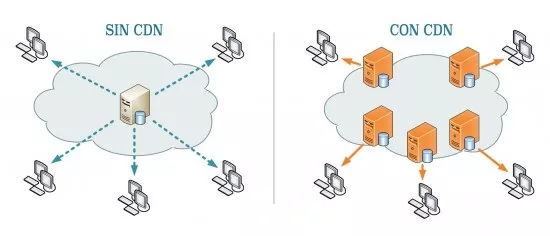
A CDN or a content delivery network is a network of servers strategically located in different parts of the world.
Each server has a copy of your web content (files, images, scripts, etc.) and serves visitors to the site from the nearest server.
Imagine a CDN as fiber optics, which travels the world and displays the contents to the web visitors of your page, not from where have hosted but from the closest server to where they are connecting, all at high speed, a way that is very effective and has very low latency.
A CDN is structured as a network of servers. This means thousands of servers hosted in data centers with a lot of bandwidth, always more than you have in your hosting provider.
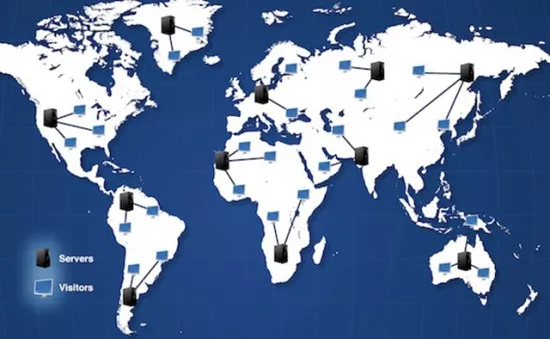
These data centers are strategically distributed across the globe, to deliver content from the minimum possible distance to all users worldwide.
Data centers usually located in regions with the highest number of Internet users. These data centers are often called POP or Point of Presence.
Logically, a CDN with a large number of POPs should deliver content faster to users. As you can imagine, the more users there are connected, the more POPs there are, so most are usually in the United States, Europe, and the Far East, and there are fewer in Africa and South America.
How does a CDN work?
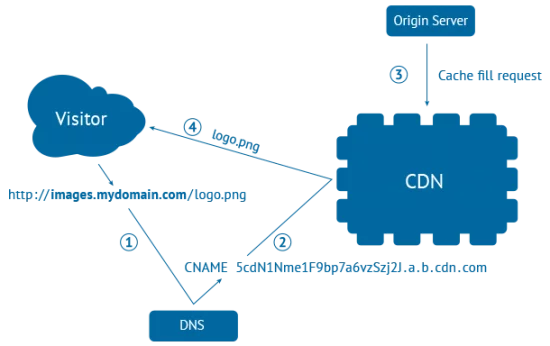
It seems that nothing has changed in computing but it is so in some things because basically, a CDN works in a structure of client-server, and in fact, this is how it is better understood its operation.
The client-server model of a CDN
The client-server model is a representation of the “request-response” network model.
1. You, the client, request part of the content. The webs are hosted on servers, which are only specialized computers dedicated to hosting websites. In these servers, there is a software called web server that is the one that takes care to host, manage and serve your web. This server software is usually Apache, IIS or NGINX, sure that some sounds to you, and if not, your web will be managed by some of these web server software.
Consequently, a web server and a server are two different entities. A web server is a software that resides on the hardware, the server.
2. The URL you type (for example yourwebsite.com) is the resource identifier, so-called Universal Resource Locator in the webserver.
3. The web server uses the URL to find the resource, which is most often an HTML page. If the page exists, it responds to the client “in a few seconds”.
4. If the web server does not find the resource then it offers a response error known as “404 page not found”.
In short: on the client-server model, you (the customer) you request a page, the web server (server) searches for the resource and responds to the page.
Have you never seen it that simple?
How do the CDNs accelerate the websites?
We have already made it clear that the content is hosted on a server and served to the visitor from a request and that this task is performed by the webserver. Now imagine a situation where your server is located in India and the visitor of your web is from California to more than 12 thousand kilometers. Something will influence, right?
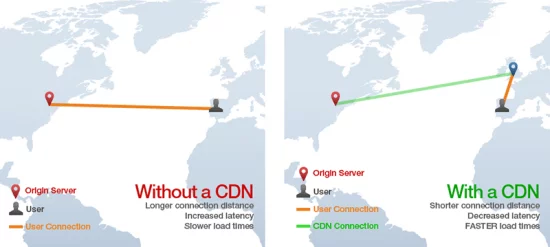
No matter the speed of your Internet connection, data travels more than 12,000 kilometers to get to the computer (or other devices) of visitors, and that requires a few seconds, whatever you put yourself.
To reduce these times and serve your content faster, websites use CDNs.
The CRC makes copies of the static content of your website and places a copy in each of their POP. Thus, when a client requests a specific resource the data is served from the POP geographically closest to the applicant (the visitor).
So, neither more nor less, is how a CDN gets your web load faster.
Other benefits of using a CDN
In addition to speeding up the loading of your website in an important way, a CDN also brings another series of benefits to your website:
- Distributes and balances the load on your server so that it can withstand high traffic volumes.
- By delegating the task of delivering CDN static content to your server focuses on the generation of dynamic content, that’s what it’s for what you use WordPress. The task of serving the result and the static contents is done by the CDN.
- Consumption of bandwidth of your server is reduced significantly since most of the heavy work is done by the CRC. This results in better times than known as uptime.
- You eliminate the geographical barrier when serving your content across the globe, especially if you offer content for other countries and want to load and position as good as in your own location.
- Incidentally, the CDN also block spammers, scrapers, and false bots and protect your web from DDoS attacks.
- You save a lot of money, since the memory and resources on servers have high prices, while you can use a CDN for very little money or even for free and with a much higher performance.
Are you still thinking about it?
Who uses CDN?

Most of the major websites use existing CDNs. Google and Microsoft have their own data centers, where they manage their own CDNs. Other sites like Facebook or WordPress.com, as well as any high traffic website that you know use CDN services. All my websites, both own and customers, take advantage of the virtues of the CRC.
We hear a lot about “cloud services” and think that they are almost always based on CDN, servers hosted across the globe that serve content “from the cloud”, but from which is closer to you.
There are several types of CDN, as in everything, and you have high-level CDN services like Akamai and others for all budgets like CloudFlare or Amazon Cloud. You even get free as offered by the Photon module JetPack plugin CDN, because actually uses the CDN for WordPress.com, or the free version of CloudFlare, more than enough for most blogs and websites of low to medium traffic.
So using a CDN is not limited to high traffic sites, in fact, any website can benefit from using a CDN, also yours, and it reviews the previous point of the “other benefits” of using a CDN.
A CDN is not a luxury, it is currently a necessity.
Okay, do I really need a CDN?
Look what it costs you.
If it has not been clear enough in the above points, I must remind you that a CDN offers enormous benefits for your web, let alone for your business online.
Especially if your site offers much static content such as images, documents or computer graphics, you should start using a CDN. This will ease most of the load on your hosting server and will serve your static content in an ultra fast way to your visitors, which will result in a better user experience and, incidentally, less cost.
As your website grows, traffic will increase and you will need to move it to higher-level servers – and price – or even to dedicated servers, as requests to your web server increase. A CDN will allow you to postpone this kind of expensive updates.
Do you have an online store? As you serve a lot of images and the success of your eCommerce and therefore paying your bills, it depends largely on user experience and speed of delivery of content. Go, check out the first point we have discussed in this article, yes, that called “Do I need a CDN?”.
How do I use a CDN with WordPress?

Do not worry. Most NSC currently offers service to websites created with WordPress, including by facilitating the configuration through plugins. You have a good example of this in the official WordPress.org plugin repository.
Normally you first register in the service, add your web, make the changes in the server, and then install a plugin for specific adjustments.
Most CDN services work through CNAME records, which means that sometimes you will have to create new records (usually for www) in the DNS management section of your web hosting, but there are others that use a reverse proxy, with services like Managed WordPress Hosting, you have a CDN that comes for free instantly without making any changes, one click. Incidentally, it offers the exclusive Railgun technology so that the connection to the hosting servers is even faster.
In conclusion

Since most of the websites let alone online businesses are geared towards a global audience, the use and popularity of CDNs is growing. By the way, the price of this type of services is increasingly competitive, not to mention if you can take advantage of any of the free solutions.
Therefore, today, it would be almost stupid not to exploit the virtues of using CDN services for websites of any size and traffic.
The choice is simple, you just have to choose the pill:
Blue Pill: To live in the world of ostrich while the rest of the world moves forward, a slow web that will not grow globally and provide a poor user experience, slow load times and your SEO be penalized in the SERP.
Red Pill: Internet face reality and take action, have an ultra fast web served globally, providing an excellent user experience, serving content at breakneck speeds and improving your SEO in the SERP.
They tell me out there that there are people who are still thinking about it, Are you one of them?